Mechanical water pump
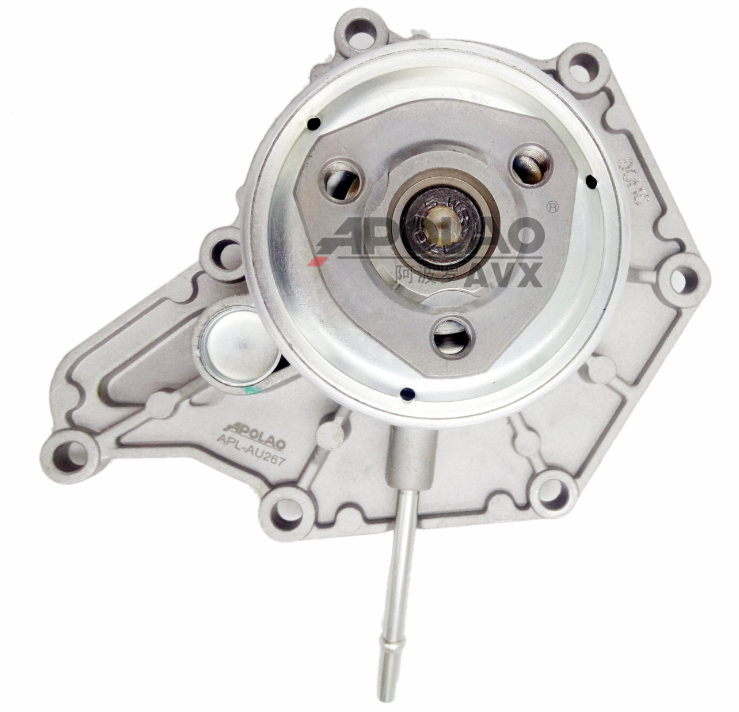
Mechanical water pump
Working Principle: A mechanical water pump drives the pump shaft and impeller via a pulley. The coolant in the pump is driven by the impeller and, under centrifugal force, is flung toward the edge of the pump housing. This generates a certain pressure and flows out through the outlet or pipe. At this point, the impeller in the pump body is at low pressure. The pressure differential between the pump inlet and the center of the impeller causes the coolant in the water tank to be drawn into the impeller through the inlet pipe, completing a reciprocating coolant cycle.
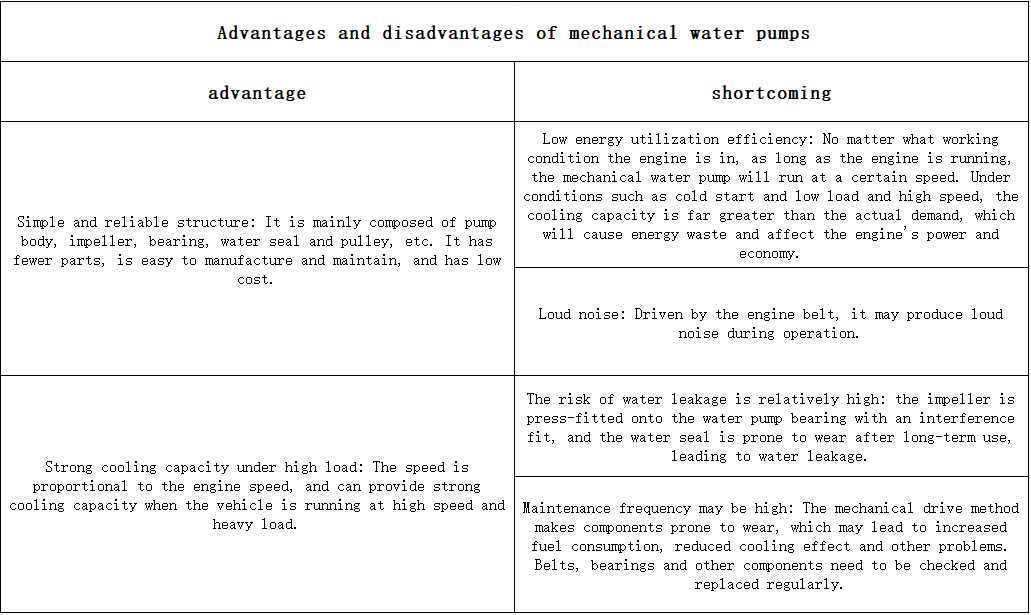
Structural composition: A typical centrifugal mechanical water pump is mainly composed of a pump body, impeller, bearings, water seal and pulley.
Working characteristics: The speed of the mechanical water pump is directly proportional to the engine speed. When the vehicle is running at high speed and high load, the cooling capacity is strong; however, under cold start and low load and high speed conditions, even if the engine does not require a high cooling flow rate, the mechanical water pump still needs to be driven by high power, and the cooling capacity is far greater than the actual demand, which will cause energy waste and may also affect the engine’s power and economy.
 electronic water pump
electronic water pump
Working Principle: The electronic water pump is driven by a motor. Upon receiving a cooling signal, the vehicle’s ECU sends a command to the control module to rotate the motor, which in turn drives the impeller. This creates a low-pressure area at the center of the impeller, drawing coolant in and forcing it out through the outlet, thus achieving coolant circulation. The ECU uses PWM to adjust the duty cycle based on feedback signals such as water temperature, precisely controlling the speed of the motor-driven impeller and, in turn, the coolant flow rate.
Structural composition: Mainly composed of pump casing, impeller, sealing ring, motor casing, electrical plug, motor assembly, bearing, rotor, controller, control seat, back cover, etc.
Operating Characteristics: The electronic water pump can start and stop based on coolant temperature and other requirements, precisely controlling coolant flow. Compared to mechanical water pumps, it can reduce pump displacement by approximately 60%. Its electric drive reduces frictional work, resulting in a fuel consumption reduction of approximately 2% in the NEDC cycle. Furthermore, the electronic water pump offers advantages such as accelerated warm-up, long service life, reduced leakage risk, flexible control, and multiple protections (overtemperature, overvoltage, overcurrent, etc.).
The following two pictures are about the advantages and disadvantages of mechanical water pumps and electronic water pumps